Union: Combine two objects together - this is sometimes referred to as addition.
- Substance 3D home
- Home
- Getting started
- Interface
- Create with Clay
- Create with Primitives
- Get started with primitives
- Primitive parameters
- Organize primitives
- Organize your scene
- Export Mode
- Render mode
- Technical support
- Release notes
- V1.22 (Current release)
- V1.21
- V1.19
- V1.18
- V1.17
- Public Beta V1.21.50 (Current release)
- Public Beta Archive
- V1 Archive
- V0 Archive
Booleans
Booleans, or boolean operations, are a common and useful 3D tool. Thanks to the signed distance field technology that Modeler is built with, booleans are very performant and easy to use.
In Modeler, a boolean operation uses at least two objects:
- The boolean object has the operation assigned to it and is recolored to reflect that. For example, when using the Union operation, the boolean object is colored green.
- The target object is any object that intersects the boolean object. There can be multiple target objects for a given boolean operation, since the boolean object can overlay multiple targets.
Boolean refers to a set of operations that can be performed with 3D objects:
-
-
Difference: Use the boolean object to cut away from target objects - this is sometimes referred to as subtraction.
-
Intersection: Delete everything except where two objects overlap.
-
Split: The target object is split into separate objects based on the boolean objects surface.
For the Union operation to apply clay to an existing layer, you first need to select the layer before applying the boolean operation. With no layer selected, the Union operation will automatically add clay to a new layer instead.
The image below shows the results of performing each boolean operation with shapes A and B. Note that for the Difference operation, B is the boolean object and is subtracted from target object A.
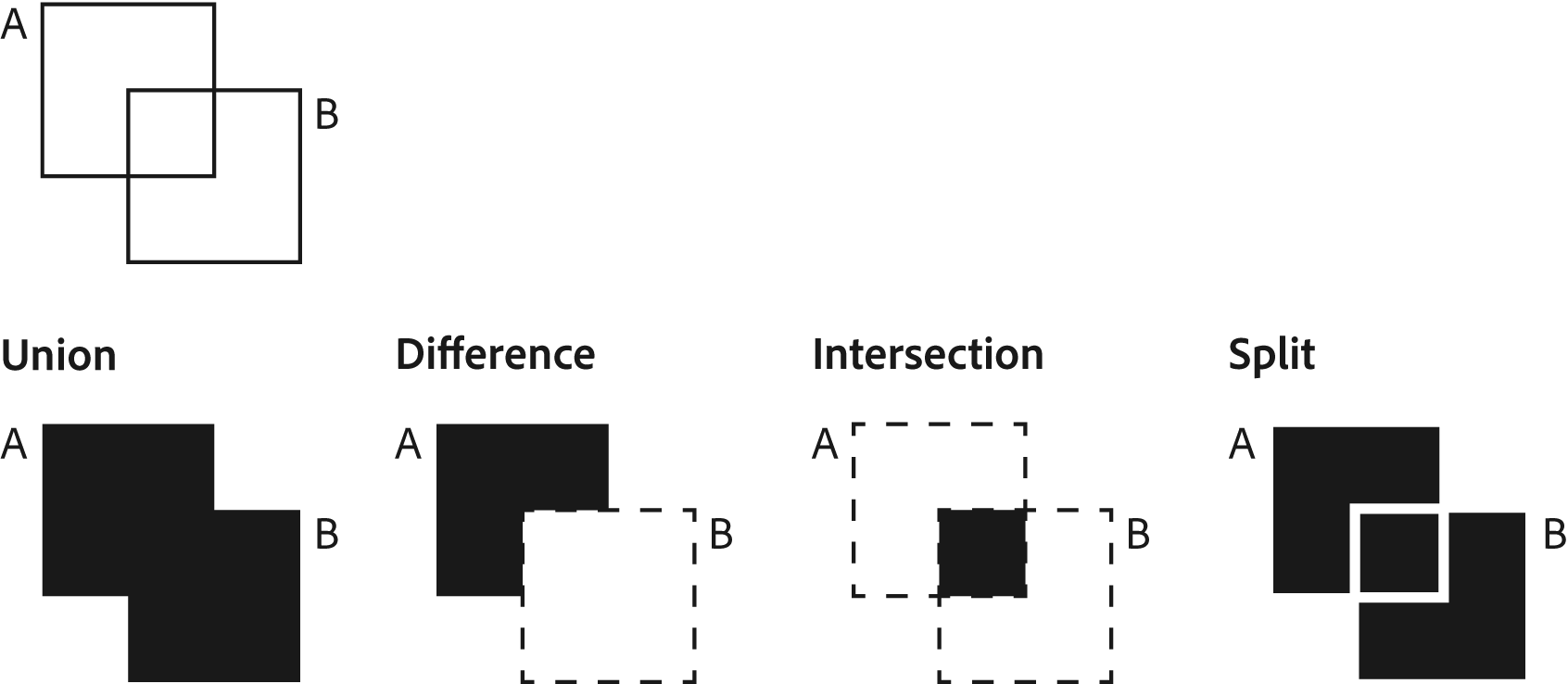

Boolean operations are available under the Booleans tab of the Actions menu. The Boolean icons match the diagram above.
Start using booleans
Booleans can only be used when not scoped into a layer. In order to use boolean operations:
- Ensure you are at group or scene scope.
- Use the Select tool to select a layer or group.
- Open the Actions menu.
- Select the Booleans tab.
- Select a Boolean operation.
- Notice that the selected object changes color:
- Red for Difference.
- Magenta for Intersection.
- Green for Union.
- Select the boolean object.
- Position the object so that it intersects another object.
- Apply the boolean operation.
- 💻Use spacebar or tap Apply in the Shortcuts panel.
- 🥽Use T1.
- You can move and apply the boolean operation repeatedly.
- Once you are done, turn off the booleans.
- Open the Actions menu and select Clear under the Boolean menu.
- This will turn the boolean object back into a normal group or layer.
Live Boolean Preview
Live boolean preview provides a dynamic preview of how some boolean operations will impact existing clay. You can toggle Live boolean preview on in the Actions menu while objects are set to act as boolean operators. You can also turn on Live boolean preview in the Preferences menu.
Art examples
Vladimir Petkovic pushed booleans to their limits to create this spacecraft.

