- Adobe XD User Guide
- Introduction
- Design
- Artboards, guides, and layers
- Shapes, objects, and path
- Text and fonts
- Components and states
- Masking and effects
- Layout
- Videos and Lottie animations
- Prototype
- Create interactive prototypes
- Animate prototypes
- Object properties supported for auto-animate
- Create prototypes with keyboard and gamepad
- Create prototypes using voice commands and playback
- Create timed transitions
- Add overlays
- Design voice prototypes
- Create anchor links
- Create hyperlinks
- Preview designs and prototypes
- Share, export, and review
- Share selected artboards
- Share designs and prototypes
- Set access permissions for links
- Work with prototypes
- Review prototypes
- Work with design specs
- Share design specs
- Inspect design specs
- Navigate design specs
- Review and comment design specs
- Export design assets
- Export and download assets from design specs
- Group sharing for enterprise
- Back up or transfer XD assets
- Design systems
- Cloud documents
- Integrations and plugins
- Work with external assets
- Work with design assets from Photoshop
- Copy and paste assets from Photoshop
- Import or open Photoshop designs
- Work with Illustrator assets in Adobe XD
- Open or import Illustrator designs
- Copy vectors from Illustrator to XD
- Plugins for Adobe XD
- Create and manage plugins
- Jira integration for XD
- Slack plugin for XD
- Zoom plug-in for XD
- Publish design from XD to Behance
- XD for iOS and Android
- Troubleshooting
- Known and fixed issues
- Installation and updates
- Launch and crash
- Cloud documents and Creative Cloud Libraries
- Prototype, publish, and review
- Import, export, and working with other apps
Learn how to create complex shapes by combining groups of objects using Boolean operations. Also, learn how you can mask an object with any shape such as a rectangle or an ellipse.
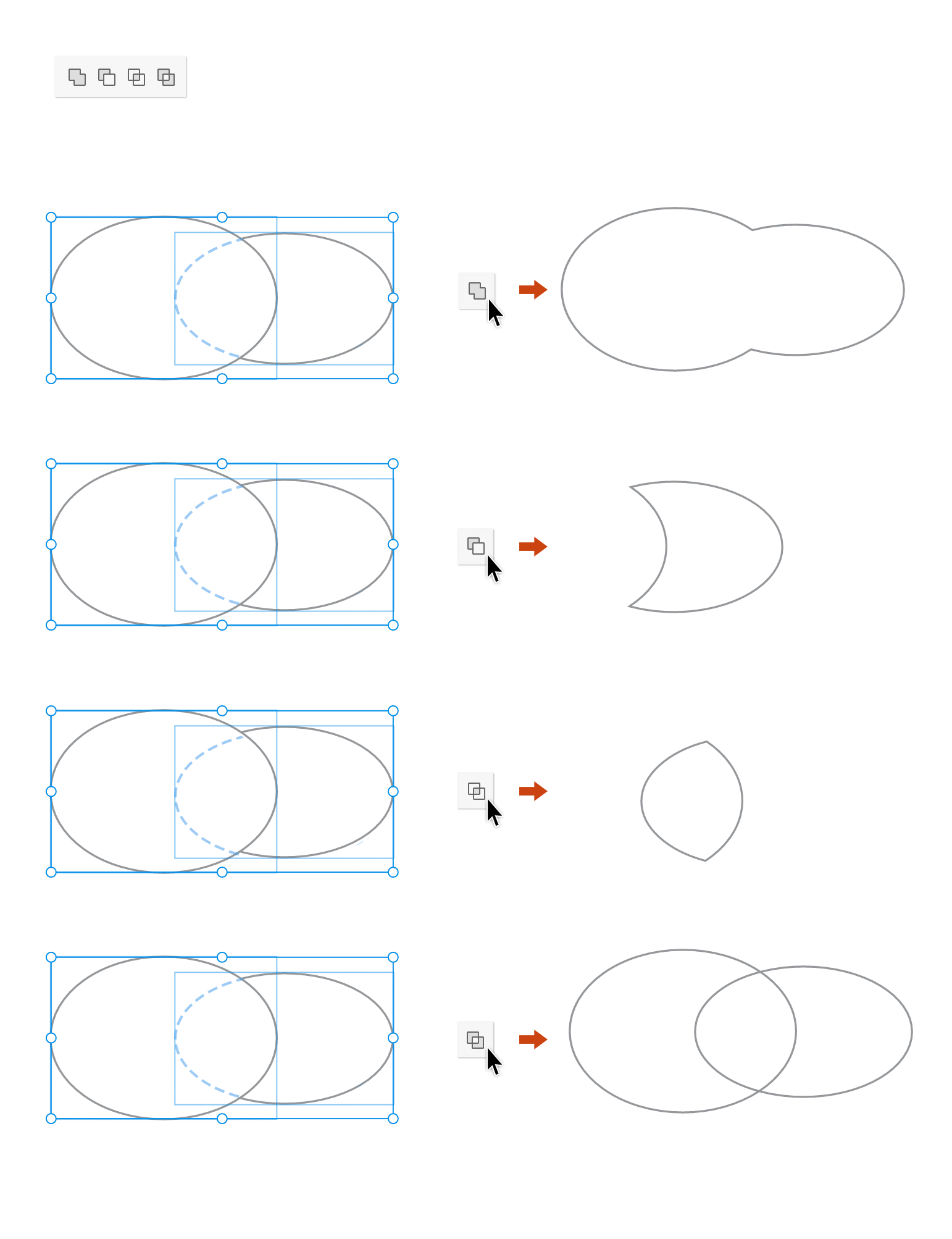
Combine objects using Boolean operations
You can combine simple shapes to create compound shapes and objects. Select the shapes that you want to combine and use one of the following options in the Property Inspector:
Add to Shape Area
Adds the area of the component to the underlying geometry.
Subtract from Shape Area
Cuts out the area of the component from the underlying geometry.
Intersect Shape Areas
Uses the area of the component to clip the underlying geometry as a mask would.
Exclude Overlapping Shape Areas
Uses the area of the component to invert the underlying geometry, turning filled regions into holes and vice versa.

Mask objects
Masking helps in hiding or revealing parts of an image. Intelligent use of masks can help you draw focus on required parts of an image, or blur or sharpen an image or change opacity of layers. You can use masks to get circle icons from a square or rectangle image.
You can also use masks to hide portions of images, and vector objects. Consider a scenario where one vector object needs to be masked with another. In this case, the top object in the stack acts as a mask.
Want to learn how to use masks to hide portions of your object? For more information, see Create a mask with shapes.