Choose File > Create > PDF From File.
- Acrobat User Guide
- Introduction to Acrobat
- Access Acrobat from desktop, mobile, web
- Introducing the new Acrobat experience
- What's new in Acrobat
- Keyboard shortcuts
- System Requirements
- Download Adobe Acrobat
- Download Acrobat | Enterprise term or VIP license
- Download Acrobat 64-bit for Windows
- Install Adobe Acrobat Reader | Windows
- Install Adobe Acrobat Reader | Mac OS
- Install updates for Acrobat and Reader
- Update your Acrobat to the latest version
- Download Acrobat 2020
- Release Notes | Acrobat, Reader
- Workspace
- Workspace basics
- Opening and viewing PDFs
- Working with online storage accounts
- Acrobat and macOS
- Acrobat notifications
- Grids, guides, and measurements in PDFs
- Asian, Cyrillic, and right-to-left text in PDFs
- Adobe Acrobat for Outlook
- Set Acrobat as default PDF viewer
- Explore Acrobat tools
- Workspace basics
- Creating PDFs
- Editing PDFs
- Edit text in PDFs
- Edit images or objects in a PDF
- Rotate, move, delete, and renumber PDF pages
- Edit scanned PDFs
- Enhance document photos captured using a mobile camera
- Optimizing PDFs
- PDF properties and metadata
- Links and attachments in PDFs
- PDF layers
- Page thumbnails and bookmarks in PDFs
- PDFs converted to web pages
- Setting up PDFs for a presentation
- PDF articles
- Geospatial PDFs
- Applying actions and scripts to PDFs
- Change the default font for adding text
- Delete pages from a PDF
- Edit a signed PDF | FAQ
- Scan and OCR
- Forms
- PDF forms basics
- Create a form from scratch in Acrobat
- Create and distribute PDF forms
- Fill in PDF forms
- PDF form field properties
- Fill and sign PDF forms
- Setting action buttons in PDF forms
- Publishing interactive PDF web forms
- PDF form field basics
- PDF barcode form fields
- Collect and manage PDF form data
- About forms tracker
- PDF forms help
- Send PDF forms to recipients using email or an internal server
- Combining files
- Combine or merge files into single PDF
- Rotate, move, delete, and renumber PDF pages
- Add headers, footers, and Bates numbering to PDFs
- Crop PDF pages
- Add watermarks to PDFs
- Add backgrounds to PDFs
- Working with component files in a PDF Portfolio
- Publish and share PDF Portfolios
- Overview of PDF Portfolios
- Create and customize PDF Portfolios
- Sharing, reviews, and commenting
- Share and track PDFs online
- Mark up text with edits
- Preparing for a PDF review
- Starting a PDF review
- Hosting shared reviews on SharePoint or Office 365 sites
- Participating in a PDF review
- Add comments to PDFs
- Adding a stamp to a PDF
- Approval workflows
- Managing comments | view, reply, print
- Importing and exporting comments
- Tracking and managing PDF reviews
- Saving and exporting PDFs
- Security
- Enhanced security setting for PDFs
- Securing PDFs with passwords
- Manage Digital IDs
- Securing PDFs with certificates
- Opening secured PDFs
- Removing sensitive content from PDFs
- Setting up security policies for PDFs
- Choosing a security method for PDFs
- Security warnings when a PDF opens
- Securing PDFs with Adobe Experience Manager
- Protected View feature for PDFs
- Overview of security in Acrobat and PDFs
- JavaScripts in PDFs as a security risk
- Attachments as security risks
- Allow or block links in PDFs
- Edit secured PDFs
- Electronic signatures
- Sign PDF documents
- Capture your signature on mobile and use it everywhere
- Send documents for e-signatures
- Create a web form
- Request e-signatures in bulk
- Collect online payments
- Brand your account
- About certificate signatures
- Certificate-based signatures
- Validating digital signatures
- Adobe Approved Trust List
- Manage trusted identities
- Printing
- Accessibility, tags, and reflow
- Searching and indexing
- Multimedia and 3D models
- Add audio, video, and interactive objects to PDFs
- Adding 3D models to PDFs (Acrobat Pro)
- Displaying 3D models in PDFs
- Interacting with 3D models
- Measuring 3D objects in PDFs
- Setting 3D views in PDFs
- Enable 3D content in PDF
- Adding multimedia to PDFs
- Commenting on 3D designs in PDFs
- Playing video, audio, and multimedia formats in PDFs
- Add comments to videos
- Print production tools (Acrobat Pro)
- Preflight (Acrobat Pro)
- PDF/X-, PDF/A-, and PDF/E-compliant files
- Preflight profiles
- Advanced preflight inspections
- Preflight reports
- Viewing preflight results, objects, and resources
- Output intents in PDFs
- Correcting problem areas with the Preflight tool
- Automating document analysis with droplets or preflight actions
- Analyzing documents with the Preflight tool
- Additional checks in the Preflight tool
- Preflight libraries
- Preflight variables
- Color management
- Troubleshoot
- Troubleshoot PDF printing in Acrobat and Acrobat Reader
- Adobe Acrobat license has either expired or not been activated
- Edit PDF forms created in LiveCycle Designer
- Insufficient data for an image error on Adobe Acrobat
- Resolve errors related to the AcroCEF/RdrCEF processes of Acrobat or Acrobat Reader
About geospatial PDFs
A geospatial PDF contains information that is required to georeference location data. When geospatial data is imported into a PDF, Acrobat retains the geospatial coordinates. With the coordinates, you can view and interact with the PDF to find and mark location data.
Geospatial data can be either vector or raster based or a combination of both. After you import geospatial data into Acrobat, you can use the data in a variety of ways:
Find and mark location coordinates.
Measure distance, perimeter, and area.
Change the coordinate system and measurement units.
Copy location coordinates to the clipboard, and then use them to show locations in several web mapping services.
Create geospatial PDFs
You can create a geospatial PDF in one of these ways:
Opening a geospatially enabled TIFF (GeoTIFF) or JPEG 2000 file
Georegistering a PDF map or scan of geospatial data
When you open an imported file, measurements, point position, and length are displayed in geographic coordinates, which you can change, measure, and mark up. You can also assemble a PDF map from a variety of sources.
Open GeoTIFF and JPEG 2000 files
GeoTIFF files and JPEG 2000 files are raster images that you can import as new documents or as new layers to an existing document. Acrobat preserves the geospatial coordinates embedded in the file. These files retain their geospatial data when they are imported. If you import these files to existing documents, their coordinate system is converted to the coordinate system of the document.
-
-
Select the geospatially enabled file to import.
-
Select settings, and then click OK.
Import shapefiles
You can import a shapefile as a new layer to an existing PDF. The shapefile must overlap with the current PDF map. Otherwise, it is not imported. If it overlaps only partially, only the part that overlaps the current PDF is imported.
A shapefile consists of several files with differing filename extensions. Acrobat requires both the SHP file and the DBF file for importing.
-
Open a PDF map, and choose View > Show/Hide > Navigation Panes > Layers.
-
Select Option on the Layer sidebar and click Import As Layer.
-
Browse to the SHP file and select it.
-
Click Settings and change the Line Properties to a solid line and the line color to blue.
Interact with geospatial PDFs
When you open a geospatially enabled PDF, you can find locations, measure distances, and add location markers. You can also copy coordinates to the clipboard for use with a web mapping service.
View the geospatial measuring tools by choosing Tools > Measure.
Use the Geospatial Location tool to perform these tasks:
View latitude and longitude while the cursor is over an area containing geospatial information.
Mark a location with a geospatial annotation.
Search for a location in a document.
Find map locations
-
Open a geospatial PDF and choose Tools > Measure > Geospatial Location tool.
-
Right-click inside the map, and then click Find A Location.
-
Type the latitude and longitude values (degrees, minutes, seconds, or decimal) in the two text boxes, and click Find.
If at least one location is available, the location is highlighted with a blue square and the page is centered on the highlighted location.
-
If the PDF includes more than one map, click the Next or Previous button to view additional results, if any. Multiple locations are available in several situations:
When a document contains multiple maps (for example, if a PDF contains a smaller map within a larger map, such as a city within a map of a state or country). When you search for a location within the city, Acrobat finds it in both the larger map and the city map.
When a document contains multiple pages of a map (for example, if page one is a map of a country and page two is a map of a state or city within the country).
-
(Optional) To add a comment (such as a place name or address), click the location marker, and then add the information in the comment box.
-
To end the search, right-click inside the map. Then select Hide Location Search, to remove the search boxes.
Mark geospatial locations
-
Open a geospatial PDF and choose Tools > Measure > Geospatial Location Tool.
-
Move the mouse pointer over the document to view latitude and longitude values of areas that contain geospatial information. Right-click inside the map, and then do one of the following:
To find a location, click Find A Location. Type the latitude and longitude values, and click Find.
To mark a location with geospatial information, click Mark Location.
-
(Optional) To add a comment (such as a place name or address), click the location marker, and then add the information in the comment box.
Measure distance, perimeter, and area on maps
When you open a geospatial PDF, the Acrobat measuring tools read the geospatial information and measure distance and area instead of page or object dimensions. Use the measurement tools to calculate distance, perimeter, and area on any geospatially enabled PDF. As you move the mouse pointer over content in the document, snap markers are shown that indicate that you are on a path or path end point. You can also see the latitude and longitude of your cursor location when the mouse pointer is over geospatial content.
-
Choose Tools > Measure > Measuring Tool.
-
In the Measurement Tool display, select a measurement type: Distance
 , Area
, Area  , or Perimeter
, or Perimeter 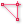 .
. -
Select a snap-to option:
Snap to paths
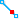
Snap to end points

Snap to midpoints

Snap to intersections

-
Do one of the following:
If you are using the Distance tool, click where you want to start the measurement, and then drag to the end point and click again. The distance is displayed in the lower-right corner.
If you are using the Perimeter tool, click the map in one corner of the perimeter, and then drag to each corner. Click at each corner and then double-click at the end point. The information window displays the perimeter size.
If you are using the Area tool, click the map at one corner of the area, and then drag to another corner. Click before changing directions. Double-click at the end to display the total area.
-
To finish the measurement, right-click and select Complete Measurement. Or, select Cancel Measurement.
Copy location coordinates to the clipboard for use with a web mapping service
After you find a location on a geospatial PDF, you can copy the coordinates to the clipboard. From the clipboard, you can paste the data into a web mapping service that reads latitude and longitude coordinates.
-
Choose Tools > Measure > Geospatial Location Tool, and then right-click the location on the map and choose Mark Location.
-
Open the location annotation and copy the location information.
Acrobat copies the data in this format: latitude then longitude, separated by a space. Paste the data into the address bar of a web mapping service that can interpret the location data.
Change measurement units within a document
To change the type of measurement units, right-click inside the map with the Measuring tool and choose Distance Unit or Area Unit. Then select a measurement type.
Change geospatial measuring preferences
You can change the measurement units for all geospatial PDFs in the Preferences dialog box. Click Measuring (Geo) from the Categories section.
Enable Measurement Markup
Adds a label to a geospatial measurement. When Enable Measurement Markup is selected, choose Use Label, and then type a label for measurements.
Snap Settings
Select the path parts to which you want measurements to snap to.
Display Value As
Determines how latitude and longitude values are calculated. Choose Decimal to display latitude and longitude as a decimal fraction. Choose Degrees, Minutes, Seconds to divide each degree of longitude into 60 minutes, each of which is divided into 60 seconds.
Display Direction As
Choose between Signed and Named. Named direction displays an N (north) or S (south) next to the Latitude, and an E (east) and W (west) for Longitude.
Always Display Latitude And Longitude As WGS 1984
Select to ensure that latitude and longitude use the current standard reference frame for earth (World Geodetic System 1984). For older maps that were drawn with an earlier grid (such as NAD 1927), you can deselect this option to see the original values. When an older map is registered in its native coordinates, coordinate positions can be different from current standards used in GPS devices and web mapping services.
Use Default Distance Unit
Select the measurement unit to use.
Use Default Area Unit
Area can be measured using a different unit from distance.
Don’t Show Transparency Layer In GeoTIFF And JPEG 2000 Images
Raster image formats include a transparency layer that you can choose to remove.
Export location and measurement markups
You can export geospatial location and measurement data to an FDF file. Each geospatial annotation has a GPTS entry. The entry corresponds to the latitude and longitude for each of the annotation points. The types of information that can be exported include the following:
Marked locations entered by using the Geospatial Location tool
Distance, perimeter (compound distance), and area measurements entered by using the Measurement tool over geospatial content
Geospatial data can be exported by using the Comments List panel.
-
To export all comments, open the Comments List panel (Tools > Comment) and choose Options > Export All To Data File.
-
To export a subset of the comments, select the comments and choose Options > Export Selected To Data File. Type the filename and click Save. The FDF file is saved.